If you're looking to buy or sell items online in Pakistan, free classified websites can…
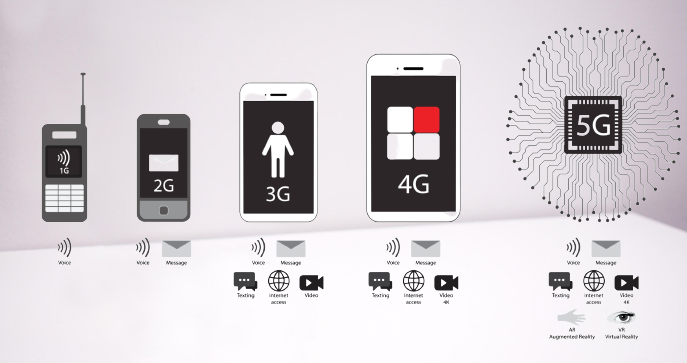
Internet generations? Basic Component 1G, 2G, 3G, 4G and 5G
The Internet generations or mobile phone generation is a cellular communication network according to the numeric generation, which are 1G, 2G, 3G, 4G, and 5G. 4G technology is fully developed, and 5G is gaining traction.
Formally, in internet generations means, G stands for “generation’’ and numeric denotes the generation number like 1, 2, 3, and so on.
Whenever we connect our mobiles to the internet, internet speed depends upon the strength of the signal that has been displayed on the home screen of the mobile, right next to the bar of signals in the form of alphabets like 2G, 3G, 4G, etc.
advertisement
Along with these positive developments, the growth of the internet has also given rise to various generations of viruses and malware like GoBrut botnet, stealthy viruses, Trojan horse malware, and sometimes common computer glitches. As technology continues to advance, new types of malware and viruses will inevitably emerge.
However, In today's digital landscape, where the threat of malware and viruses grow large, effective cybersecurity practices are essential for eradicating these malicious entities. so, everyone should have how know about cybersecurity awareness and some cybersecurity tips to stay safe online from cyber attackers.
In this set of the internet generation, each has its own requirements and organizations. Each generation has its responsibility of specification for standardization, including latency, access system, core network, bandwidth, etc.
1G - First Generation

1G was the first internet generation of mobile technology in this world.
Who introduced 1G technology?
This very first generation of commercialized cellular networks was launched in early 1970 by an engineer named Martin Cooper. It was launched by Telecom, which is known as Telstra today. Australia utilized it as the first cellular mobile network as a 1G analog-based system.
advertisement
That was the first wireless device capable of two-way communication through 1G. In this generation, mobile networks generally had poor-quality calls like voice issues and sometimes experienced dropped calls. The mobile battery had poor life. The maximum speed of 1G was 2.4 Kbps.
advertisement
1G was used in the 1980s and was later replaced by digital telecommunications 2G. First-generation had AMPS (advanced mobile phone system), TACS (total access communication system), J-TACS (Japanese Total Access Communications System), and C-Netz technology standards.
It also has FDMA (Frequency Division Multiple Access) and TDMA (Time Division Multiple Access) combinations for radio access technology.1G mobile networks now have become obsolete.
2G - Second Generation

Who introduced 2G technology?
2G was launched in 1991 by Radiolinja in Finland. When mobile phone networks shifted from 1G to 2G, they received a major upgrade. The main advantage of 2G was that its network was digital, while 1G was an analog system.
Behind this generation, the main motive was to acquire reliable communication and secure channels.
The ILOVEYOU virus in 2000 was a notable example, spreading via email and causing extensive damage worldwide.
2G implemented the approach of GSM (Global System for mobile communication) and CDMA (code-division multiple access). 2G was the first to introduce many fundamental network services such as text messaging as SMS and MMS, conference calls, internal roaming, call hold, and billing services, among others.
advertisement
The second generation of the mobile network was primarily divided into two technologies. One is TDMA (Time division multiple access) which includes a global system of mobile networks. The other 2G slice is the CDMA which is now less in use due to GSM.
The highest speed of a 2G network with GPRS is 1Mbps or 50 Kbps with a boost of data rates for GSM. The disadvantage of 2G is that it is very dependent on the nearness and location of towers. The only way to overcome that problem is through its digital nature.
From 2G to a 3G wireless network, the major leap was 2.5G and 2.75G interim standards to assist the next generation that is less known.
3G- Third Generation

Third-generation (3G) mobile telecommunication is expected to provide multimedia qualities to mobile phones as well as easier and faster wireless communication with “anywhere, anytime” service.
Who introduced 3G technology?
3G was introduced in 2001 by the international telecommunication union ITU and NTT DoCoMo in Japan. early research was started in the 1980s and its standers and specifications was continues for 15 years. however, the technical applications were launched in 20001.
However, in the initial launch, this 3G technology had a low pace of post-adoption that can be attributed to various factors like lack of network security, high development cost, newer tower installation, traffic handling capacity, etc.
The standard specification set of 3G is divided into two groups worldwide. One is 3GPP and the other is 3GPP2. The 3GPP specification of 3G is focused on developing the GSM core network which is known as UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications Systems), and access technologies of radio.
On the other hand, the 3GPP2 specification of 3G is, on the other hand, developed for the CDMA2000 standard system and CDMA access. In both, the 3GPP specification is extensively used.
advertisement
The improved qualities of a 3G system over their forerunners have introduced many applications with high data rates like video on demand, mobile TV, Telemedicine, video conferencing, and location services.
Data rates also permit users to browse the web on their mobile phones. The maximum speed of 3G is 100 Kbps or 0.1 Mbps, which is 30 times faster compared to 2G. Some connections of 3G can achieve a 7Mbps speed.
However, 3G took time to gain worldwide acceptance, but it also paved the way for the growth of smartphones. Subsequently, it is not wrong to say that the introduction of the iPhone was on the rise in 2007 when 3G gained worldwide adoption.
4G- Fourth Generation

4G is the fourth generation of a wireless network of mobile phones that was replaced by 3G.
Who introduced 4G technology?
4G was launched in 2009 in Sweden and Oslo. The 4G standard was set by the international telecommunication union (ITU), which was later used as the international mobile telecommunication advanced (IMT).
The main technologies that have advanced and made it easier are multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) and Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM).
The standard aims of 4G are to be spectrally efficient, able to support smooth handover, offer high-quality services (QoS), and be based on an IP-switched network. The speed of 4G is higher than 100 Mbps which is enough to assist the high quality of multimedia streaming.
advertisement
Due to lower latency, 4G also has a preferable response time as compared to 3G. The download speed in this generation network has also improved, which means that a mobile connected to 4G will receive a faster response than a mobile connected to 3G.
In the context of 4G internet generation, C++ programming language has been instrumental in enabling the development of applications and systems that harness the capabilities of this advanced mobile communication technology.
Another advantage of 4G is that it is vastly used in the VoLTE (voice over LTE) industry. It provides a much clearer and more stable connection for calls, making internet-based business easier.
5G - Fifth Generation

Who introduced 5G technology?
5G is the fifth generation of mobile networks, launched in April 2019. South Korea is the first nation to adopt 5G on a large scale. All devices that Caries 5G used are Ericsson, Samsung, and Nokia base equipment.
In addition, there are currently nine enterprises that sell radio hardware carrying a 5G system. These are the Cisco system, Altiostar, Ericson, Telecom, Qualcomm, Huawei, Samsung, ZTE, and Nokia.
5G is the next generation of mobile networks which is rolling out after 2G, 3G, and 4G.
It provides a faster speed of connection and streaming than all previous generations. Also, 5G gives greater multi-Gbps data speed, enhanced capacity, ultra-low latency, and lower response time.
These are all capabilities in specification and requirements that make them superior to all previous generations. The 5G mobile network expands the traditional network to industries like automotive.
advertisement
Conclusion
As the wireless journey of internet generations is updating day by day, the modems' processing power is also increasing. As the generation bit rates become greater, the data becomes more capable of being delivered across all active components, from the cell site through the core network.
Guys, it is now clear that while you are browsing, the speed of your connection depends on the signal strength indicated by the alphabets 2G, 3G, 4G, etc.





















Kinza Rao – Associate Software Engineer